Anyone who wants to make a right decision needs information. This information has a very strong effect on financial market where managers and stock holders rely on such information in order to make important decisions. Usually a large amount of information not only can’t help decision makers, but also make them confused and nervous.
The effect of information systems and accounting software on transparency of financial statement information
Mehdi Beedel
Department of Economics and Management, University of Isfahan, Isfahan, Iran
Abstract
Anyone who wants to make a right decision needs information. This information has a very strong effect on financial market where managers and stock holders rely on such information in order to make important decisions. Usually a large amount of information not only can’t help decision makers, but also make them confused and nervous.
Information systems can be helpful to solve such problems. In this paper we evaluated the effect of information systems and accounting soft wares on the financial statement transparency. To do so, 86 brokers from 110 brokerage active in Tehran Stock Exchange were surveyed. Analyzing the results derived from the questionnaires showed that the information systems and accounting soft wares have a significant effect on three main characteristics of financial statement transparency which are being relative, reliability and comparability.
Key words: Accounting information systems, Accounting soft wares, Financial statement transparency, Decision making.
Introduction
Nowadays, information is one of the most important resources that anyone uses to make different decisions.
Information is exponentially increasing in all of the frame works and millions of people use it in order to make decisions. People try to find the best source of information that can satisfy them in the best way. A good source gives brief and useful information.
A wide part of information is unusable or unrelated. This problem is highlighted more and more in financial environments (Boockholdt, 1999). In the financial markets anyone who reach related information can make the best decision and gain the profit while others may lose their money because of using unsuitable or unrelated information (Brigham et al., 1996).
In addition, managers also need related and reliable information which can help them to make right decisions.
Generally, decisions in business environments are being made for different purposes such as: customer’s satisfaction, higher quality, lowers wastes and so on.
At the same time, the most important purpose for any company, manager or employee is increasing profit while reducing costs which leads to increase the stockholders wealth (Ross et al., 2002).
To achieve such purposes, managers should use accounting and financial information to make the right decision. Accounting in general, is trying to measure and give economical information about a company or industry to the users. The users (managers, stockholders, governments, and so on) try to make right judgments and analysis this information.
In order to do that, they should get related and reliable information throw a wide amount of information. Accounting is an information system and managers should get reliable and high quality information from formal or informal resources (HoIIander et al., 1999). On the other hand, information technology and accounting information systems have a major role in wasting time and placing limitations, helping the users to gain updated and suitable information quickly (HoIIander et al., 1999).
Generally, accounting information systems; 1) provide financial reports on a daily and weekly basis and; 2) provide useful information for monitoring decision-making process and performance of the organization (Dastgir et al., 2008).
Financial statements are being prepared to present financial and economical information about a firm. The information in the financial statement provides a brief and general view from a firm’s activity, even non-financial activities. But a financial statement should have some important characteristics to be useful for the potential investors, stockholders, managers and so on. These people would like to use the data in the financial statements confidently.
One of the most important characteristics any financial statement should have is transparency. It can make the users feel confidence that all the data they see in the financial statements shows a right view of the firm and they can rely on it confidently. Three main characteristics of financial statement transparency are: being relative, reliability and comparability (Simon, 2000).
Being relative: this item includes how much the information in the financial statements is useful in estimation and analyzing.
Reliability: this item includes the ability to accept the data in the financial statement and how much neutral a financial statement has been prepared.
Comparability: it includes persistency and how much the information in the financial statement are useful.
The main question is that considering the potential characteristics of accounting information systems and accounting soft wares, dose the results of using these systems have the characteristics explained above? (being relative, reliability and comparability).
In this paper it has been tried to find out if information technology and accounting soft wares have a significant effect on the financial statement transparency.
In other word, we want to answer the question “ does the results derived from accounting systems have the financial statement transparency characteristic items which are being relative, reliability and comparability that can help the users to make the best decision using such systems?”
Literature review
Recently, Vicky Arnold et al. (2012) evaluated the impact of tagging qualitative financial information on investor decision making. Participants were randomly assigned to a standard or tagged presentation of Management’s Discussion and Analysis (MD&A), the U.S. equivalent to Management’s Commentary.
Results indicate that nonprofessional investors use a more directive search strategy under the tagged condition, while professional investors’ search strategies are unaffected by the tagged condition. Saliency of risk information increases for both investor groups in the tagged condition (i.e., risk assessments and stock price predictions are more associated).
Santamaria et al. (2010) have demonstrated that IT implementation derived in a decrease of labor time and therefore a decrease in costs. Badescu and Garcés-Ayerbe (2009) have analyzed the impact of investments in IT on the productivity of Spanish firms and have found that although the firms in the sample experienced some improvement in productivity in the considered period, this improvement was not significantly derived from IT investment.
In another study Dastgir et al (2008) evaluated the effect of accounting information systems in Tehran stock exchange. The results indicated that implementation of accounting information systems at these companies caused improvement of managers’ decision-making process, internal controls, and the quality of financial reports and eventually facilitated the process of company’s transactions. However, the results did not show any indication that performance evaluation process had been improved.
Jadidi (2003) examined the effect of using information systems on Bahman automobile company’s managers. The results showed that accounting information systems had an important effect on manager’s decision making process and also could help investors, debtors and other people who use financial statements.
Donnell and Julie Smith David (2000) evaluated how information systems influence user decisions. They tried to organize a literature review of 15 journals from 1987 through mid-1999, which identified 57 decision-making studies. Their findings indicate that a wide range of opportunities was available for information systems research on issues of contemporary importance. This discussion includes changes in the decision process initiated by implementing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, data warehouses, electronic commerce, virtual organizations, on-line financial reporting, and disaggregated financial statement information.
Otley (1988) argues that Accounting Systems are important parts of the fabric of organizational life and need to be evaluated in their wider managerial, organizational and environmental context. Therefore, the effectiveness of accounting information systems not only depends on the purposes of such systems but also depends on contingency factors of each organization.
Hypotheses
After reviewing the relevant literature and according to financial statement transparency characteristics, three main hypotheses were designed as of the following:
- Accounting information systems and accounting soft wares have a strong effect on the relativity aspect of financial statement transparency.
- Accounting information systems and accounting soft wares have a strong effect on the reliability aspect of financial statement transparency.
- Accounting information systems and accounting soft wares have a strong effect on the comparability aspect of financial statement transparency.
Research methodology and sample selection
This study is based on the brokerage active in Tehran’s stock exchange. No specific time period is considered since the survey is not a time series study. A questionnaire was designed and after pilot study was sent to the sample brokerages and brokers were asked to fill in the questionnaire.
A population of approximately 110 brokerage was active in Tehran stock exchange in 2012. Our sample has been randomly selected using Morgan sample selection table.
According to Morgan sample selection table, 86 brokerage were selected. In this study, the data selection instrument is questionnaire. The questionnaire consisted of twenty four questions, which were carefully designed to collect relevant data. The questions were on the five point Likert-type questions, with a choice of very little to very much.
STATISTICAL TESTS
In the first step, the normality of the variables has been analyzed by means of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Table 1, shows the results of normality test. It shows that the normal distribution of data derived from the questionnaire is accepted.
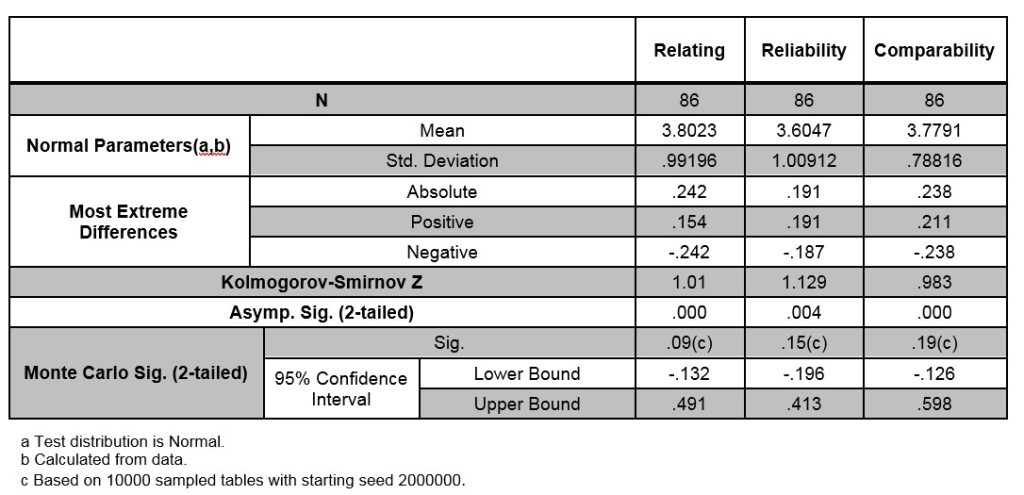
After testing the normality of data, in order to test the hypotheses, one sample T test was used at confidence level of 95%. The research hypotheses were put in the form of statistical hypotheses such as H0 and H1. for example hypothesis number one were changed to the following form:
H0: Accounting information systems and accounting soft wares have a low effect on the relativity aspect of financial statement transparency.
H1: Accounting information systems and accounting soft wares have a strong effect on the relativity aspect of financial statement transparency.
Other hypotheses were also examined like hypothesis number one. With regards to the nature of five-point scale questions, therefore, we tested whether the mean value of each question was less than or greater than 3. Number 3 was the average number of the five choices in each question:
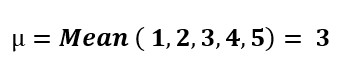
Thus, three statistical hypotheses were set up as follows:
H0: μ ≤ 3
H1: μ > 3
Testing the hypotheses and analyzing the results
As it was noted earlier, 86 brokers were selected as the research sample. The questions put forward to them in the questionnaire. Average number of 3 was taken as the mean of the five-point questions in the questionnaire. Table 2 shows a descriptive statistics of three hypotheses:
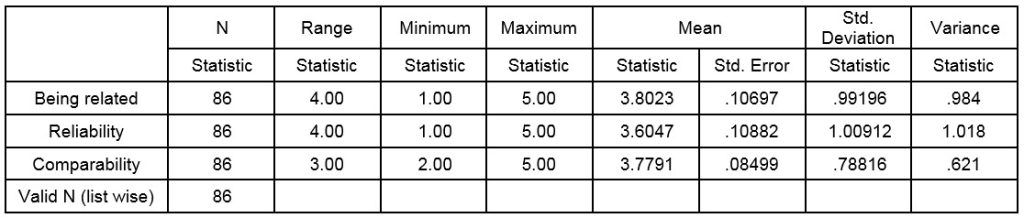
Table 3 shows the results of testing the first hypothesis.
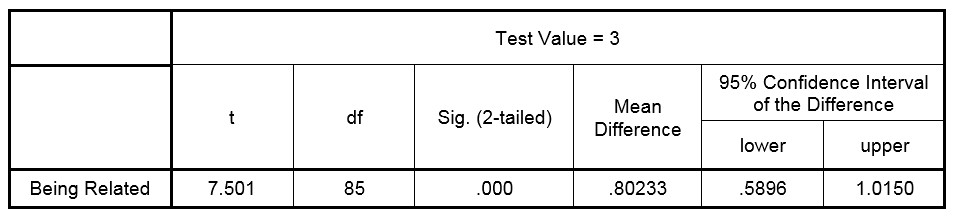
As it is clear in table 3, according to T value or the significant number (0), hypothesis H0 is rejected, therefore the hypothesis: accounting information systems and accounting soft wares have a strong effect on the relativity aspect of financial statement transparency is accepted.
Results of testing hypothesis 2 and 3 are being shown in table 4 entirely:
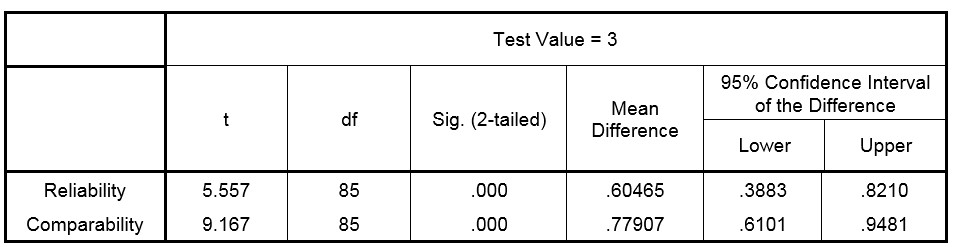
According to table 4, the significant number is 0 for both reliability and comparability hypotheses, so H0 is rejected and the hypotheses are accept. It indicates that accounting information systems and accounting soft wares have a strong effect on the reliability and comparability aspect of financial statement transparency.
Prioritizing Test:
In this part, the effect of accounting information systems and accounting soft wares on three characteristics of financial statement transparency is evaluated. In the previous parts it was shown that there is a strong relationship between using accounting information systems, accounting soft wares and three financial statement transparency characteristics which are being related, reliability and comparability. Now we prioritize the power of this relationship to find out which characteristic is being affected stronger.
In order to do that, hypotheses below were formed:
H0: µ1= µ2 = µ3
H1: µi ≠ µj at least for one i, j
(i1= being related, i2= reliability, i3 = comparability)
To test this hypothesis, Paired sample T Test was used, table 5 shows the results of this test:
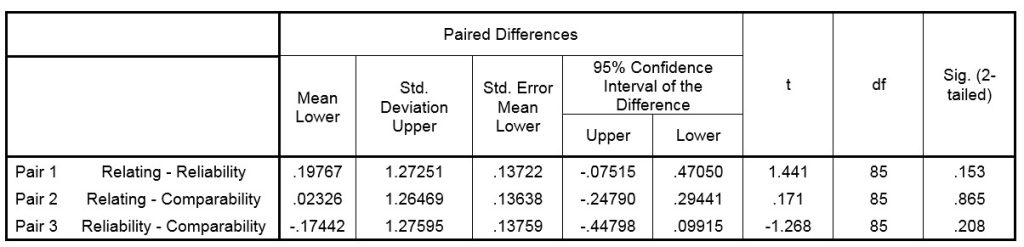
As it is clear in table 6, according to T values or significant numbers, the hypothesis H0 is accepted, that means there is no significant difference between the power of the effect of information systems and accounting soft wares on three characteristics of financial statement transparency which are being related, reliability and comparability.
But any way according to the three main hypotheses results and the variables descriptive statistics, we can figure out that the effect of using information systems and accounting soft wares on relativity aspect of financial statement transparency is a more sensible.
Discussion and Conclusions
Making a good decision needs information. Such information helps decision makers to make a decision with open eyes. Although information is very important in the process of decision making, a wide amount of information make the decision maker confused.
Decision makers need brief, related and on time information. This problem becomes significantly important in financial markets. Decision makers in this uncertain environment need useful information to make the best decision. But there is a wide amount of data in a financial environment that most of it does not have the characteristics explained before and makes the stockholders, managers and other people who use this information confused.
Accounting information systems and accounting soft wares make it easy. To preparing financial statements or presenting valuable information on a continues base during the year not only at the end of the year.
In this paper, we tried to find out how does the information systems and accounting soft wares effect one of the most important characteristics of financial statement, transparency.
Financial statement transparency includes three main characteristics: being related, reliability and comparability. Any financial statement that its data contains these characteristics is a transparent statement.
Three main hypothesis were tested separately. In order to do that, 86 brokers were selected as the research sample from approximately 110 brokerage, who were active in Iran capital market. They were asked to answer twenty four questions of a questionnaire. The results showed that using information systems and accounting soft wares leads to higher transparency and strongly effect three main aspects of financial statement transparency.
Like all of the empirical studies, the present research also has its own limitations due to the methodology employed. Use of questionnaire to collect data always has its own Limitations, since responses could be biased because of the common method used for collection of all data.
Although extensive care has been taking when designing the questionnaire and the pilot study refined the questions, still the criticism of the survey method can never be completely ignored and should be taken into account. From generalization of the results point of view, measuring research question based on the opinion of the respondents would limit our generalization of the findings.
REFERENCES
- Badescu, M., Garces-Ayerbe, C., (2009). The impact of information technologies on firm productivity: Empirical evidence from Spain, Technovation, vol. 29: 122-129.
- Bharadwaj, S.G., Konsynski, B.R., (1999). Information Technology effects on Firm Performance as measured by Tobin´s q, Management Science, vol. 45, number. 7: 1008-1024.
- Boockholdt, J.,(1999). Accounting Information Systems Transaction Processing and
Control. The Mac-Graw-Hill companies.
- Brigham, F.E,, Gapenski, L.C,, Davis, R., (1996). Intermediate Financial Management.6th edition, Dryden Pr. America.
- Chong, V., (1996). Management Accounting Systems, Task Uncertainty and Managerial
Performance: A Research Note. Accounting Organization Society, Vol.21: 430-514.
- Dastgir, M., Sadjady, H., Hashemnejad, H.,(2008). Evaluation of the effectiveness of Accounting Information Systems. International Journal of Information Science and Technology, 6, Number 2: 49- 59.
- Donnell , E.O., David, J., (2000). How information systems influence user decisions. International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, Vol.1, Number 3: 178-203.
- HoIIander, A., S, Denna, E.L., Cherrington, J.O., (1999). Accounting information Technology and the Business Solution. Advances in Accounting Information Systems,Vol.6, number 2.
- Huber, G., (1990). A Theory of the Effects of Advanced Information Technologies on
Organizational Design, Intelligence and Decision Making. Academy Management Review, Vol. 15: 47-71.
- Jadidi, A., (2001), The effect of accounting information system characteristics on decision making process ,Department Of Economics and Management, University Of Isfahan, Iran.
- Narango, GIL, D., (2004). The Role of Sophisticated Accounting System in Strategy Management, The International Journal of Digital Accounting Research, vol. 4, number.8: 125-144.
- Otley, D.,(1980), The Contingency Theory of Management Accounting: Achievementand Prognosis, Accounting, Organization and Society. Vol.5: 194-208.
- Ross, S., Westerfield, R., Jordan, B., (2002). Fundamental Of Ccorporate Finance ,4th edition, McGraw Hill.
- Santamaria, L., Nunez, M., Gago, S., (2010), The role played by interdependences in ERP implementations: an empirical analysis of critical factors that minimize elapsed time, Information & Management, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2 009.10.004.
- Scapens, R., Jazayeri, M.; Scapens, J., (1998). integrated Information Systems and the implications for Management Accountants, Management Accounting Research, vol.76, number . 8: 46-48.
- Simon, R., (1987). Accounting Control Systems and Business Strategy: An EmpiricalAnalysis. Accounting Organization Society, Vol.12, Number 2: 61-74.
- Sutton, S., (1992). Can We Research a Field We Can not Define? Toward an Understanding of the AIS Discipline, Advance Accounting Information Systems, Vol.1: 1-20.
- Tam, K. Y., (1998). The Impact of Information Technology Investments on Firm Performance and Evaluation: Evidence from Newly Industrialized Economies, Information System Research, vol. 9, number 1: 85-98.
- Vickey, A., Bedard, J., Philips, J., Sutton, S., (2012). The impact of tagging qualitative financial information on investor decision making: Implications for XBR, International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, Vol.13, Number 1: 2-20.



No comment